The WHO Meeting Yesterday Brilliantly Concludes With Probing Question: How Will WHO Mitigate Obvious Dangers Of Their Digital Health Open Source Infrastructure? WHO Stammers & Has No Real Plan…
The WHO has clearly not thought this through, as usual, and admits Digital Health Open Source Infrastructure may negatively affect States.
WHO Conference on "Complexity of Pandemics N°5 – Embracing Open Source Solutions for Health Emergencies"
1,538 views Streamed live on Jun 13, 2023
In this fifth instalment of the Speaker Series, we will discuss the relevance of Open Source approaches in digital solutions for health emergency preparedness and response. How can the application of Open Source principles improve public health technologies? What are the challenges and opportunities in “open-sourcing” digital solutions across the globe? How can communities of Open Source contributors be forged to jointly innovate technologies? How can we ensure the sustainability of Open Source technologies in the space? Our two speakers – to be announced shortly – will share stories of how they have implemented Open Source technologies for health emergency preparedness and response. The Speaker Series event will also function as a public launch event of the Open Source Programme Office (OSPO) of the WHO Pandemic Hub. The OSPO is an initiative which supports WHO as well as stakeholders from Member States, partners and academia to collaboratively develop sustainable, innovative, and impactful Open Source solutions for pandemic and epidemic intelligence. The event will be co-hosted by Charité Center for Global Health.
Key quotes IOJ noticed:
The system is apparently DECADES old:
4:45 “for those of you in the room and all of you joining us online for the fifth edition of our speaker series holding here at the Hub this is this evening this is a second one in the physical premises of the Hub where we're in um the hub for epidemic and pandemic intelligence it was set up like most of you know already to really narrow the Gap around a data collection analysis and its use for decision making and we do that through work and projects and initiatives around three broad areas firstly connecting data from different dimensions different sources for through innovating Innovation developing new tools new systems new people and thinking together how to make a best use of great new ideas emerging from around the world
“and all of this happens on the back of what we've been investing in for years on the strengthening existing surveillance systems threatening institutions around the world that have been doing exactly the same thing”
The origins of WHO & Governments “social listening” programs:
19:32 “so hi I'm Yao I am founder and CEO of odk I helped to start the project almost 15 years ago and I've been leading it ever since adjustments yes yeah yeah good adjustments adjustments adjustments we'll try this it's a collaborative effort to give these stocks so so for those who do not know it um odk is a open source platform that lets you build powerful offline forms to collect the data you need wherever it is it's basically a replacement for paper forms and surveys it's primarily used by researchers field teams me professionals.”
21:33 um so we really have incredible reach with this project and most of these users are working in social impact so domains like public health Global development crisis response climate monitoring and so on in global Health alone and I want to give you a sense of our our impact in global Health odk had incredible impact odk was the data collection platform that was used in the eradication of wat polio in Africa the clinical trial data for the recent malaria vaccine was collected with odk the verbal autopsies that mentioned the global burden of disease use odk and we are really at scale in most of the challenging regions in the world I think recently there who in afro launched a campaign to vaccinate 21 million kids in Cameroon Chad Nigeria and car and guessed it odk is sort of critical to that effort this reliability especially at scale is why I sometimes like to call odk the Land Cruiser of data collection but since this is a German audience I thought I would go with the Unimog of data collection the key takeaway here is that for offline data collection odk has sort of become the way that things are done governments have used it for years data collectors have been trained on it in their schools data managers know how to build their reports with it the app works on 22 000 different Android devices it's been translated into 60 plus languages we support the Ethiopian calendar the Islamic calendar the Myanmar and calendar has been used in cities it's been used in jungles it's been used at Sea
you might be asking has it been used by a U.S president yes of course it has Jimmy Carter called it remarkable because they use it in election monitoring
Addressing Foundational Risks:
1:23:33
My name is Mustafa Hunter founder president of Health governance International and I would for this reason ask about what is the governance component or government several governance components that coming here and how do you think of it because they're different. I can spot like corporate governance for such companies where you would like put this bullet on how you govern them the governing structure within the minister of health and the public data governance um
security risks and governance related risk
and added with all these things flowing down how this data things in is that an integrated system around the funnel use the term Foundation like because this has to go hand in hand
otherwise this whole structure it's like if you're building a building but without a strong Foundation a building the bigger it goes the riskier it would collapse you know
1:24:34 yeah it's a great it's a great question and I'll start by just just saying for for many people who have been observers of the digital Health space there's been a general lamentation that that why has digital Health not scaled and when you examine a little more closely
you see that these these massive constructs of of digital Health implementations have been put into place without adequate attention to those foundations right and so it's no surprise that a a 15-story building collapses when you haven't paid attention to those fundamental investments in strategy in policy in in governance that that needs to be in place to manage those systems for the long run.
1:25:15 let me actually turn to you and and ask you from the the Tunisian example um how did you go about putting together the governance model as you go through the digital transformation
O.K. So based on the above, they ADMIT:
“these massive constructs of of digital Health implementations have been put into place without adequate attention to those foundations”
OK WHO. Got it. Understood. The foundation is weak for Digital Health.
Tunisia then explains how their Digital Health open source pilot system works:
1:25:27 for our experience for this implementation uh we are convinced that for its success we need uh to have an infrastructure we need also to interconnect all the different Health actors involved in the surveillance system and in the health and in the healthcare system with these fragmented information system and different levels of maturity regarding I.T infrastructure we are also convinced that one of the main points that we have to put in place is to have a legal legal framework for health and Proclamation exchange between the different the different actors in order to ensure a reliable data data sharing… (they go into many details)
Discussing the perceived risk of of Government investment in open source software:
27:41 a question around the perceived risk of of Open Source and I think one of the the the challenges in a public procurement process is these these lasting misunderstandings of what is it we're actually buying when it when government chooses to invest in an open source software?
1:28:00
Q: How do we de-risk the the understanding of of Open Source in in government procurement channels?
that's a that's a a tough question I think in many ways
1:28:16
we need to think about how we “professionalize” open source…
…open source sort of comes from a from a culture and from a time where you have a lot of volunteers and amateurs who are who are building software because they have a real passion for it, and that passion has led to solutions that are really powerful and flexible, impactful, so much so that governments are forced to just really seriously consider it. And on our side as software developers are folks who who lead open source projects it's our responsibility to make that easier for governments in some way…
1:29:02 …
so you will see a lot of projects these days partnering with with open source foundations having a legal team having a marketing team as a way to sort of “professionalize” this…
How they plan to pitch the open source Digital Health scheme to your government using threat and coercion:
1:29:46 (OPEN SOURCE ENGINEER SPEAKING) on the government side you know I for me it's just crazy that we have to explain to governments that infrastructure has costs… like roads cost some amount of money and these are digital roads.
It's not a one-time cost
if you don't invest in a road over time it'll crumble
[gibberish and second guessing himself] um and so uh for me using the term digital infrastructure um should make it very easy, but it has not been easy, and so there's more work to be done. But we are stubborn in the open source world and so certainly I'm not giving up anytime soon and I hope my you know my brothers and sisters in open source won't either
but that's what we need to do.
We need to convince governments that these are digital infrastructure that is critical for performing in a modern world and
if you don't invest in this infrastructure you will be in a position where you are subject to the whims um of of a corporation, you will not have ownership over your uh your your people's data.
WHO explains little known details:
49:53 “efforts in this presentation in this slide sorry I will try to summarize a little a bit the the challenges that we are struggling for this romance implementation so mainly the behavior change because users are used to use paper-based system the sustainability the human resources and also the financial resources, the turnover of focal points…
51:35 Alan lebreak is the director of The Who Department of digital health and Innovation he and his team are leading efforts to build resources and the WHO smart guidelines that will make it easier to adopt and Implement Open Standards and WHO guidance to be incorporated into open source digital Health Solutions.
Allen is the founding director of the Johns Hopkins University Global M health initiative and the editor-in-chief of the Oxford open Digital Health Journal.
He's an infectious disease and population epidemiologist and served until September of 2022 as a professor and the inaugural associate chair for research in the department of international Health at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Allen has also served as a tech technical advisor to several International and Global Health agencies and ministries of health [IOJ WILL FOIA WHICH ONES] and he was the chair of the WHO digital Health guidelines Development Group and a member of The Who digital Health roster of experts
Digital is about Primary Health Care.
Digital is about Universal Health Coverage.
Digital is about pandemic resilience and building strong Health Systems and for us at WHO, digital health is a is a core pillar of of how we support member states in their journey to achieve universal health coverage and and health for all.
um we are the Secretariat:
not many people might know this in the room but WHO serves as a Secretariat for the global strategy on digital Health which is a member state document that articulates a vision for transformation of Health Systems leveraging digital between 2020 and 2025.
…we even built on the success off that amazing work that the the European commission has done with the digital documentation of covid certificates an open source uh approach to allowing countries to exchange credentialed health information during Public Health emergencies across borders and I think I think that is an excellent example of WHO now taking on that role of of being the trust anchor for This Global Network
so that countries can exchange that trusted digital content across across these borders…
it's just the beginning because now we will hopefully see things like the digital yellow card International patient summaries, uh immunization certificates
that can be enabled by this type of Open Source infrastructure that that you both highlighted but I think we've also seen some shifts over the last few years and you you mentioned this Hajer in your comments that the pandemic has led to an acceleration of country level interest and engagement in digital transformation and and what that is is a shift it's a shift away from disconnected vertical systems towards uh uh interoperable environment that you you articulated so nicely in your uh description of Tunisia's Health System and who is getting more and more asks for this kind of support
so I think the investment in ospo and the the work that we're doing in in digital health and Innovation is really helping to address that ask from from countries, helping to provide technical assistance and support helping to frame National digital health strategies and costed road maps for action and standards-based Enterprise architecture
I think is is really critical as as our our colleagues in Tunisia have done we're also seeing reduced uh enthusiasm for for disconnected vertical hard-coded digital Solutions and that's what brings us to this conversation about open source today um where where open source Solutions enable an ecosystem of locally adapted and locally managed uh tools usually leveraging uh open source standards like hl7 fire that you mentioned is being encouraged in in Tunisia
this allows governments to source and sustain uh interconnected web of Solutions
in country growing local talent and expertise which is something that that odk I think has done wonderfully over the last decade or so um an enabling technology that has spurred hundreds of local entrepreneurial and social Enterprises and and I think facilitated the the conditions for countries to be in the driver's seat when it comes to their own digital transformation so so these are the key descriptors of what we're seeing coming down the road from our vantage point at who not only open source but Open Standards and these being local adaptable and extensible software platforms and standards that can meet the needs of governments in peace and uh and emergency times as as we like to put it
17:31 expert advisor to the open source program office or the gospel a lawyer by training and involved in intellectual property and public licensing models for over 15 years a member of the council for the legal Network at the free software Foundation Europe and a fellow at the open Forum Europe Katarina maraki “This goes back to the licensing issue that katharina just mentioned meaning that it has a license on how a code can be covered and used then individuals and organizations or governments can safely experiment because the legal risk is mitigated and so in the context of Public Health emergencies this can mean the difference between deploying a piece of software when you know a disease or some other outbreak is something small and localized it's an epidemic or as we saw with covid it turns into a pandemic”
*end excerpts*
Well there you have it folks! The ultimate plan to one world open source digital health monopoly, where the health monopolies control your data. They’ll know what you eat, how you sleep, what you watch and which angle you wipe your ass every day! Let us know if saying “ass” is too “crass”.
Basically sums up that they don’t know what they’re actually doing and have zero risk assessment, which basically means it’s another experiment on the global population.
God forbid if they put our data in the hands of Big Government overseen by the WHO/UN allowing them to control your private health data with their AI.
There is way more than this but we would be here forever dissecting this transcript instead of getting the job done and stoping these megalomaniacs. Watch the video and read the transcripts for yourself if you are inclined to do so.
If you are overwhelmed and want to help but do not know where to start, or what is really going to cause real change just know there are options for you to support!
You can be the thorn in the side of tyranny by assisting IoJ in the battle for freedom by commenting, sharing and making a generous donation!
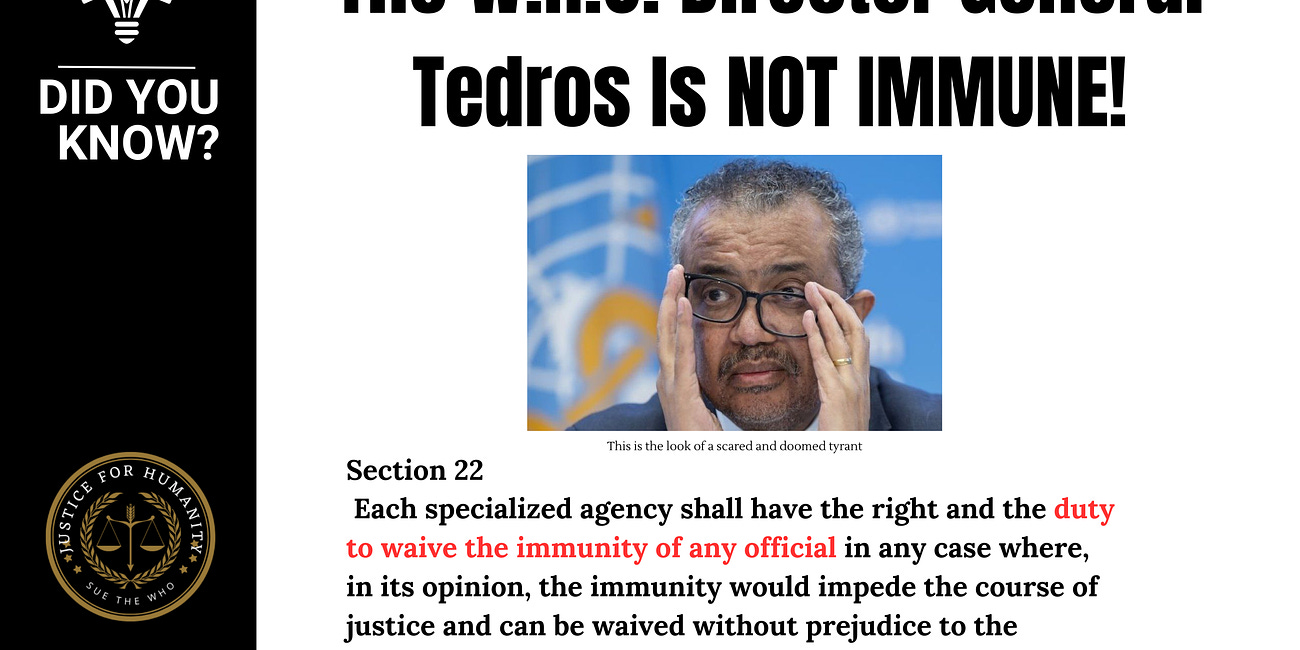
IOJ is at the forefront of the fight and tip of the spear against the globalist WHO tyranny! If you want to see Tedros prosecuted, fired and force your country to leave the WHO then support the good people working on that day and night…
IOJ HAS FILED CHARGES FOR CRIMES AGAINST HUMANITY AND THE WHO WENT INTO HIDING. ALL NATIONS ARE BEING ALERTED.
SPREAD THE TRUTH THAT THE WHO IS IN DISHONOR AND BREACH OF FUNCTIONS REFUSING TO ANSWER TO CRIMES.
IT WILL BE THE EASIEST WAY TO MAKE ALL NATIONS EXIT THE WHO, BY SHOWING THE BREACH OF DUTIES. READ MORE BELOW:
Why be the resistance when you can be the PERSISTENCE?












They also aren't considering how much more EMF radiation will be emitted globally with all those devices constantly online.https://romanshapoval.substack.com/p/emf101
The details of the crimes (very good); https://bailiwicknews.substack.com/p/make-murder-a-crime-again?utm_source=post-email-title&publication_id=37889&post_id=128769710&isFreemail=true&utm_medium=email